Preliminary results of the "Japanese Longitudinal Study of Children and Parents (JLSCP) 2023"
Comprehensive analysis of factors related to children's "sense of happiness"
Related factors include relationships with parents and friends, school life and learning situations, and self-perception
The Institute of Social Science at the University of Tokyo (Location: Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo; President: Teruo Fujii) and the Benesse Institute of Education, an in-house think tank of Benesse Corporation (Headquarters: Okayama City; President: Hitoshi Kobayashi), launched a joint research project to clarify the present aspects of "Everyday Life and Learning of Children" in 2014.
Multiple surveys were conducted for nine years since 2015 of the same pairs of parents and children (approximately 20,000 pairs from 1st-12th grade students) to identify changes in their attitudes and behaviors. The OECD (Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development) Learning Framework 2030 has set a goal of "achieving individual and collective well-being" for the future education system under "The Future of Education and Skills 2030." In addition, the "Fourth Basic Plan for the Promotion of Education" approved by the Japanese Cabinet in June 2023 states "improving well-being rooted in Japanese society" as one of the directions of the education policy. Complying with these requisites, in the present project, we analyzed the factors related to children's "sense of happiness"--whether they feel "happy now" and "can be happy in the future" from various perspectives.
Consequently, we found that the parents' sense of happiness and involvement with their children were related to their children's "sense of happiness." Further, self-perceptions of school life, friendships, learning situations, and self-confidence are significant factors associated with the "sense of happiness." Thus, children's "sense of happiness" is related to diverse factors. We would like to use this analysis as a starting point for our project, to think together with many others about what we can do to realize a society in which children and their parents feel happy.
- The figure shows the results of a multiple regression analysis conducted with children's "sense of happiness" ("sense of happiness score" in Figure 0-2) as the dependent variable and each factor as an independent variable.
- This is the analysis result of the 'Survey on Children's Life and Learning' in 2023 (of children from 4th to 12th grade). For more details, please refer to Figure 6.
Main Survey Results
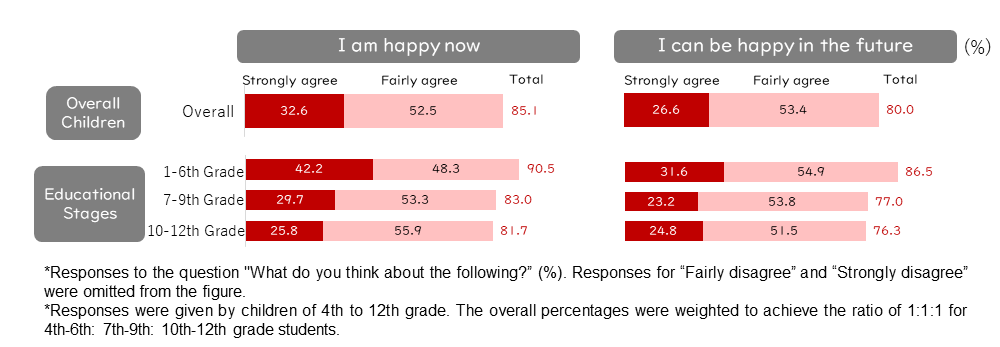
⓪Data on "Feelings of Happiness"In this section, we present the data on the "sense of happiness" before examining the associated factors.
- Happiness now and in the future - About 80% of respondents answered "I am happy now" and "I can be happy in the future."
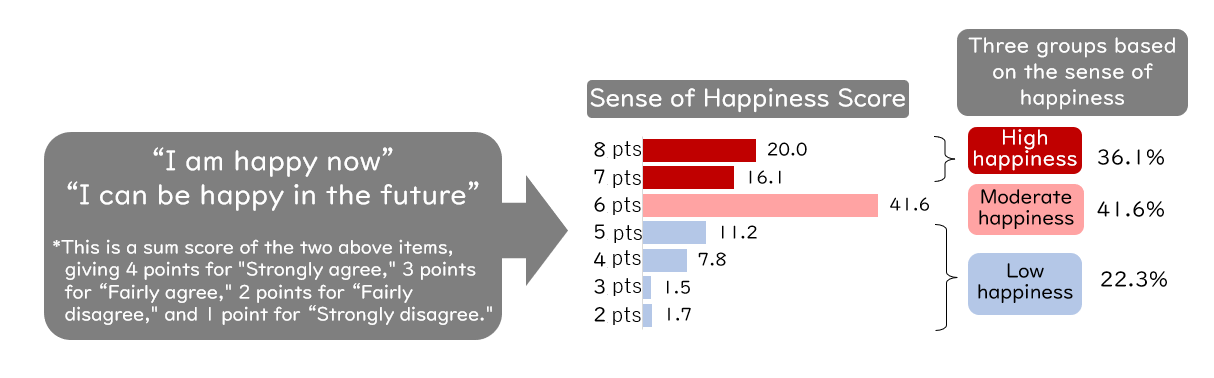
For the factors, happiness now and in the future, a majority of respondents (50%) answered "Fairly agree," followed by "Strongly agree" (30%). However, about 20% of the children answered "Fairly disagree" or "Strongly disagree" (Figure 0-1). - Happiness scores and classification of the three happiness groups
To analyze the factors associated with children's "sense of happiness," we calculated the "Sense of Happiness Score." We added the scores of two items, "I am happy now" and "I can be happy in the future," with determiners "Strongly agree = 4," "Fairly agree = 3," "Fairly disagree = 2," and "Strongly disagree = 1." Based on these scores, an index for the three groups (High happiness, Moderate happiness, and Low happiness) was created to analyze factors associated with the "sense of happiness" (Figure 0-2).
Results of Individual Associated Factors
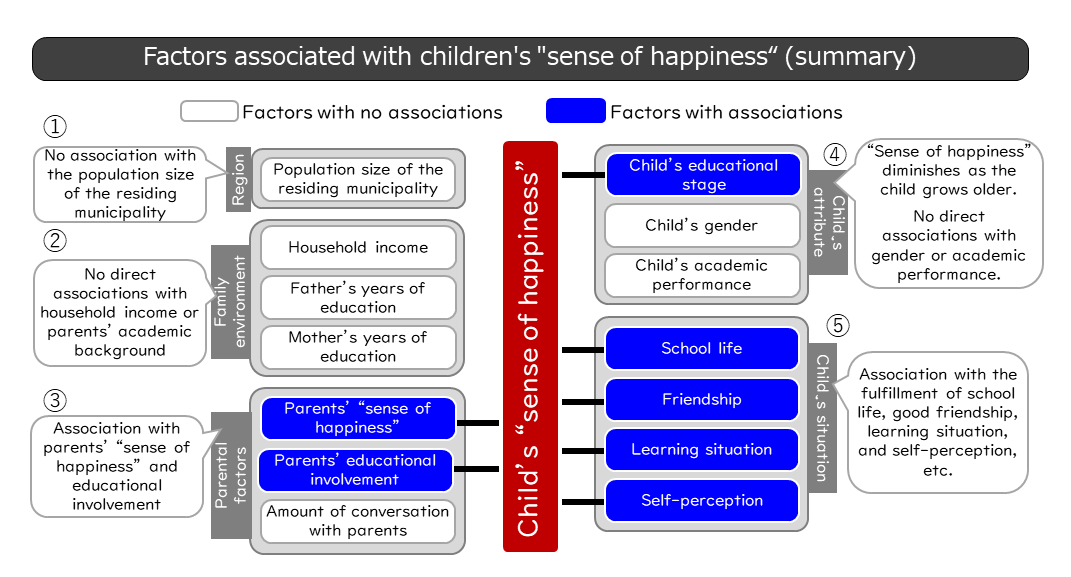
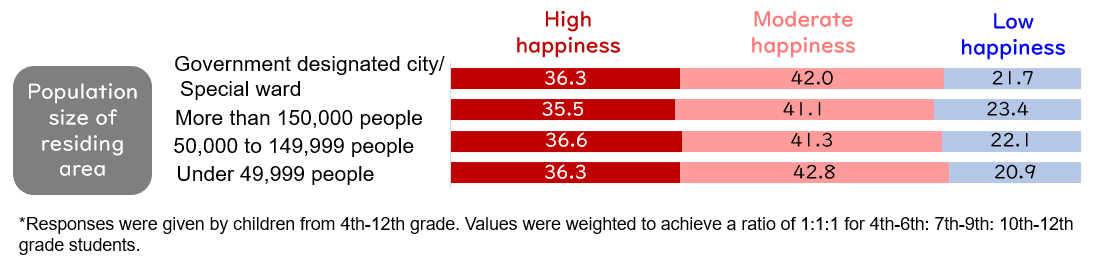
①Region - The population size of their residing area is not associated with children's "sense of happiness."The data show that the population size of the municipality where participants reside has no association with their children's "sense of happiness" (Figure 1).
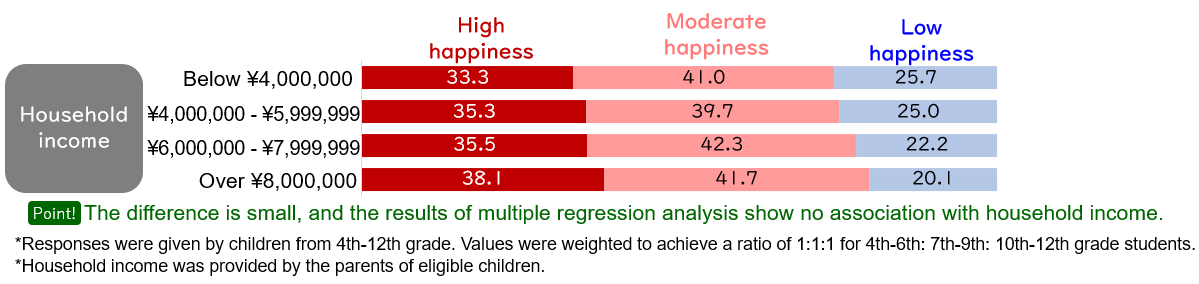
②Family environment - Family economic status and parental educational background are not directly associated with children's "sense of happiness."
When observing the relationship between the "sense of happiness" and family economic status (household income), we found that children from high-income households more often tended to be in the "High happiness group" (Figure 2). However, the difference in "sense of happiness" between different income groups is marginal, and multiple regression analysis (Figure 6) shows that it has no association with household income. Similarly, parents' years of education (educational background) were not associated (Figure omitted) with children's "sense of happiness." The differences observed in the "sense of happiness" in Figure 2 are related to parents who are more educationally engaged (Figure 3-3) and tend to have higher income and educational backgrounds. However, this factor is not likely to be directly associated with children's "sense of happiness."
③Parents' factors - Parents' own sense of happiness and educational efforts are associated with their children's "sense of happiness."
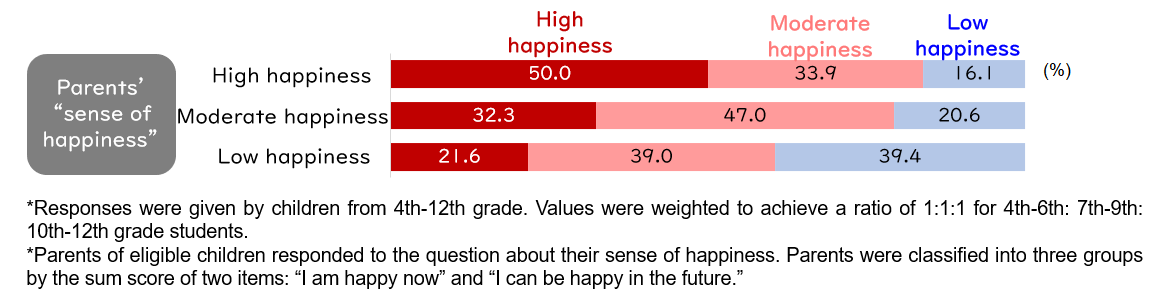
- Parents' sense of happiness - Parents and children's sense of happiness are linked.
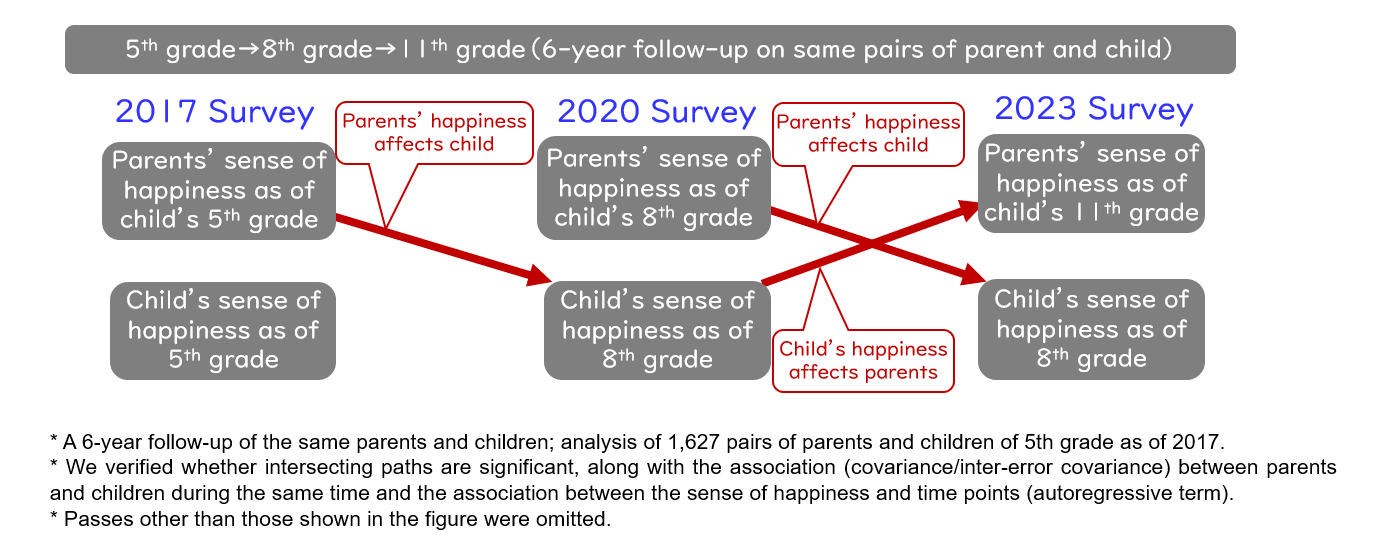
As for the parents in the "high happiness" group, fifty percent of their children are also in the "high happiness" group. In contrast, focusing on the parents in the "low happiness" group, only 20% of their children are in the "high happiness group" [Figure 3-1]. By analyzing the same pairs of parents and children every 3 years for 6 consecutive years, it was found that not only did the parents' sense of happiness affect the children's sense of happiness three years later, but the children's sense of happiness also affected the parents' sense of happiness three years later [Figure 3-2]. In other words, when parents are happy, children are happy, and when children are happy, parents also feel happy. - Parents' educational involvement - children who receive supportive involvement have a higher sense of happiness
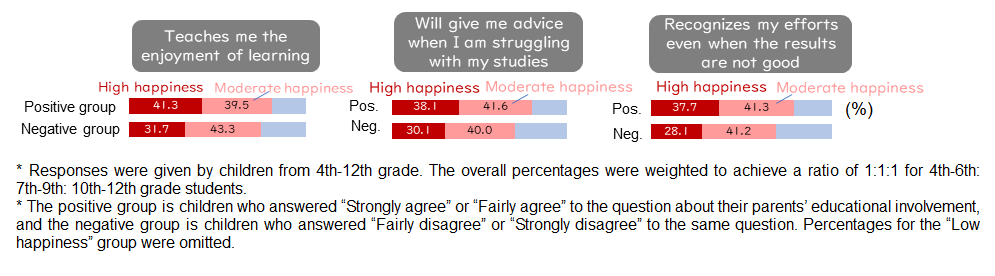
While 41.3% of the children who provided affirmative answers (positive group) to "Teaches me the enjoyment in learning" were in the "High happiness" group, 10% fewer children (31.7%) of those who denied it (negative group) were in the "High happiness" group. Children who receive supportive involvement from their parents also tend to have a higher sense of happiness than those who do not (Figure 3-3).