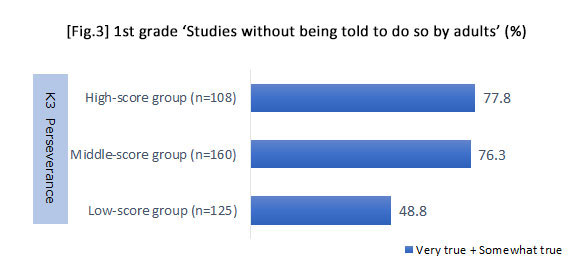Results of the fifth round of a multi-round survey capturing changes of the same children over the course of seven years (from age three to fourth grade of elementary school)
- Summary / Survey overview
- Details of survey results
- Comments from Professors who Supervised the Survey
Details of Survey Results
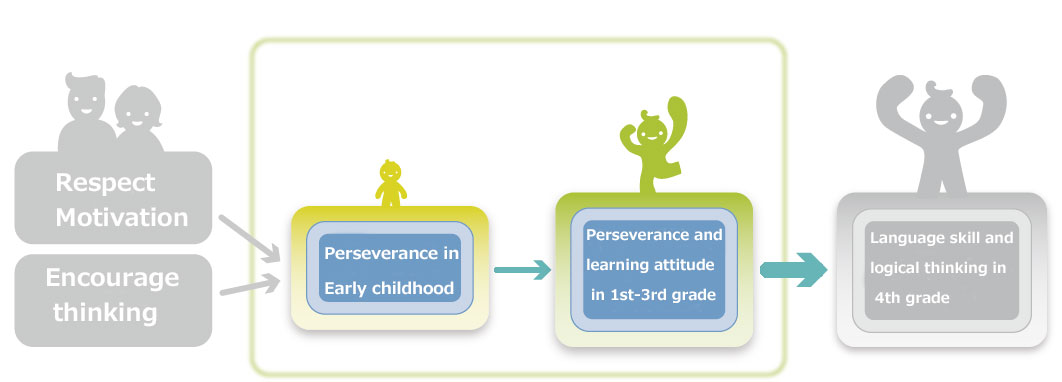
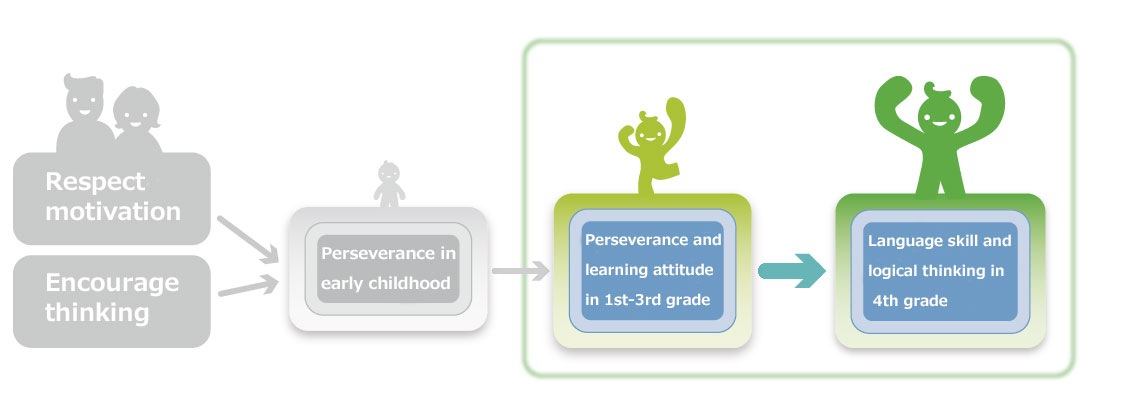
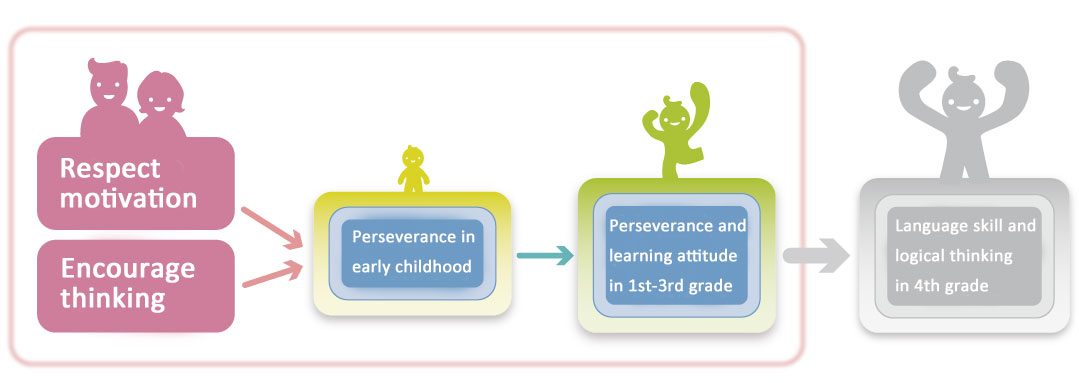
1. Children who have higher levels of "perseverance" such as 'can take on challenges without giving up easily' during early childhood tend to continue to have higher levels of learning attitudes including 'studies without being told to do so by adults' and "perseverance" during the lower grades of elementary school (i.e., first to third grade).
[Proactive learning attitude in lower grades of elementary school]
Consists of four items: 'Studies without being told to do so by adults;' 'Can stay focused until studying has been completed;' 'Can immediately start studying after sitting down at the desk;' and 'Can think and try to solve problems by themselves if they encounter difficulties in the course of their study.'
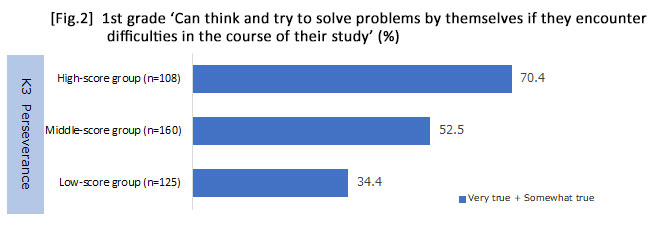
* Children who acquire higher levels of "perseverance" during early childhood including 'can take on challenges without giving up easily' and 'can try different ways to achieve goals even when things don't turn out as anticipated' tend to 'think and try to solve problems by themselves if they encounter difficulties in the course of their study' and study 'without being told to do so by adults' during the lower grades of elementary school.
Scores were applied to the items of "perseverance" and aggregated, then classified into three groups (i.e., high-, middle- and low-score groups).
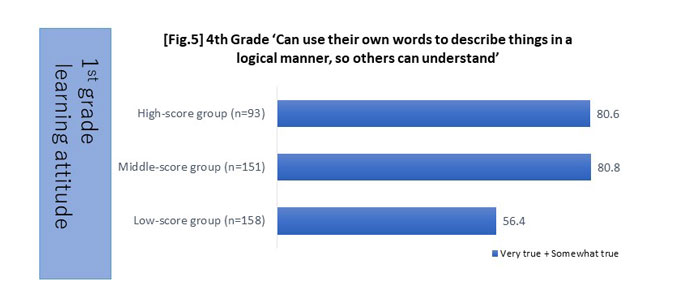
2. Children who have acquired learning attitudes and "perseverance" during the lower grades of elementary school have higher language and logical thinking skills in fourth grade.
[Language and logical thinking skills]
- Language skills: Consists of four items: 'Can take notes in an organized manner;' 'Can write kanji in correct shapes, angles and stroke order;' 'Can write sentences using subjects and predicates;' and 'Can write sentences by accurately using coordinating conjunctions.'
- Logical thinking skills: Consists of six items: 'Can use their own words to describe things in a logical manner, so others can understand;' 'Can explain their reasons saying "Because ...";' 'Can write in a logical manner;' 'Is interested in seeking patterns and rules in things that are seemingly unrelated;' 'Can consider cause and connections, and convey this to others;' and 'Can think while comparing other's opinion with their own.'
*Proactive learning attitudes such as 'studies without being told to do so by adults' and higher levels of "perseverance" such as 'can take on challenges without giving up easily' during the lower grades of elementary school lead to higher language and logical thinking skills including 'can take notes in an organized manner' and 'can use their own words to describe things in a logical manner, so others can understand' in fourth grade.
Scores were applied to the items of "learning attitude in first grade" and aggregated, then classified into three groups (i.e., high-, middle- and low-score groups).
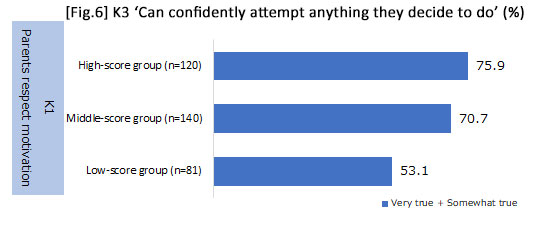
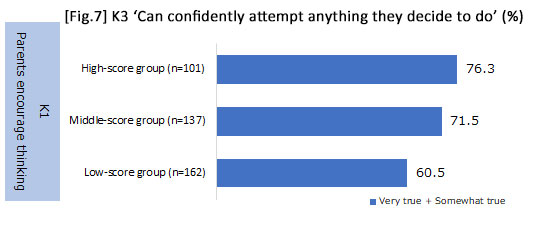
3. With regards to parental involvement, the attitude to respect the child's motivation and the encouragement of thinking (i.e., encouraging them to think for themselves) influences "perseverance" from early childhood to the elementary school period.
[Respect motivation and encourage thinking]
- Respect motivation: Consists of seven items: 'Respect and support what the child wants to do;' 'Try to understand the child's feelings no matter what the situation;' 'Allow the child to complete what they are trying to do without providing assistance;' 'Let the child do what they want without ordering him/her about;' 'Credits the child more than scold him/her;' and 'Listen to the child's say when scolding him/her.'
- Encourage thinking: Consists of four items: 'Answer the child's questions on "Why?" and "How?";' 'Encourage them to try to think for themselves when asking parents questions;' 'Encourage the child to discover different ways of playing the same game;' and 'Discuss each other's impressions after going out together.'
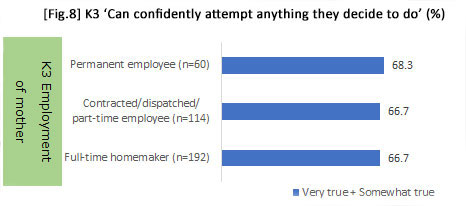
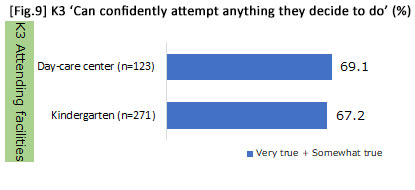
*From analyzing how "perseverance" from early childhood to the elementary school period is influenced by parental involvement, results revealed that it was influenced by attitudes toward childrearing such as respecting motivation and encouraging thinking during K1. In addition, no difference was detected between whether parents were working or not, and whether the child had gone to kindergarten or a day-care center in K3.
 |
 |
||
| Scores were applied to the items of 'encourage thinking / respect motivation' and aggregated, then classified into three groups (i.e., high-, middle- and low-score groups). | |||
 |
 |
||
| Scores were applied to the items of 'encourage thinking / respect motivation' and aggregated, then classified into three groups (i.e., high-, middle- and low-score groups). | |||